Tıbbi dedektiflik: Filyasyon
Bir hastalığın, enfeksiyon etmeninin ya da sağlıkla ilgili bir sorunun tüm dünya gibi çok geniş bir alanda yayılım göstermesine pandemi denir. Pandemiler tüm dünya nüfusunun önemli bir bölümünü etkiler. Pandemi, geniş bir alanda bir hastalığın, enfeksiyon faktörünün veya bir sağlık sorununun yayılmasıdır. Salgın anında korunma ve kontrol önlemleri alınmalıdır. Bu önlemler genel olarak kaynağa yönelik alınabilecek önlemler, bulaşma yoluna yönelik alınabilecek önlemler ve sağlam kişiye yönelik alınabilecek önlemlerdir. COVID-19 ile ilgili filyasyon çalışmaları ülkemizde indeks vakanın görüldüğü 11 Mart 2020 tarihinden itibaren büyük bir titizlikle yürütülmüştür. Bu çalışmanın amacı yapılan bazı filyasyon örneklerinden yola çıkarak Türkiye’de ve Kayseri ilinde filyasyon çalışmalarının nasıl yapıldığını anlatmaktır. Dört vaka serisi sunduk. Salgın hastalıklarla başa çıkmanın en önemli noktası, sağlık sisteminde güçlü bir altyapıya sahip olmaktır. Bir tıbbi dedektiflik örneği olan filyasyon çalışmalarının pandeminin yönetimine büyük katkı sağladığı düşünülmektedir.
Tam Metin
Introduction
A pandemic is the spread of a disease, an infection factor or a health problem in a wide area. Pandemics affect an important part of the population in the whole world.(1) The world has experienced several pandemics before and some of these are Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) which began in 2003 and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) which began in 2014.(2) The Turkish Ministry of Health has taken measures in this regard and started preparation and planning for pandemic in 2004.(3)
As it is known Corona Virus Disease-19 (COVID-19) which is now affecting the whole world has caused the death of thousands of people. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared it a pandemic on 11th of March, 2020. The first index case in our country was reported on 11th March 2020.(2) As there is no current vaccine or specific treatment method for Coronavirus disease, the measures taken are mostly for resource control and mode of transmission. Filiation is important in this regard.(3)
Protection and control measures should be taken during an epidemic. These measures are generally for resource control, mode of transmission and healthy individuals.(3) Especially investigating the contacts and/or detecting the source of infectious disease and taking the measures before it spreads more are important in the fight against the disease. Filiation activities on COVID-19 have been being performed meticulously in our country since the first index case was detected. In accordance with the measures of the Turkish Ministry of Health for the pandemic, Hospitals, Provincial and District Health Authorities, Community Health Centers, and Family Health Centers have been authorized to work on filiation.
The authorized centers work on filiation procedures in a quick way and the Ministry of Health acts in coordination with Security Forces in this regard. Moreover, in accordance with the new measures of the Ministry of Health, close follow-up of main infected cases and contacts is also provided through specific mobile applications. Fieldworks on filiation in authorized centers are performed by filiation teams and these teams consist of a physician, a healthcare officer and an assistant officer. In our country, 4,600 teams have been formed.
The teams directly reach the address of the individuals and all these actions are controlled from a single center. When the main case is detected a detailed anamnesis is obtained and the individuals (family members, co-workers, neighbors, relatives, etc.) who have had a contact with the infected case within the last 48 hours are determined before the symptoms appear. The contacts are visited and followed up. The individuals are required to self-quarantine in their home for 14 days.
They are followed up by daily phone calls and examined by family physicians. In case the contacts have symptoms they are informed about the relevant authorities to apply and legal sanctions for violations of quarantine. All the data obtained from one-to-one interviews are collected in a shared electronic information system.(2) Filiation activities are mostly performed by family physicians and public health specialists. The occurrence of symptoms especially in individuals in contact with the infected person is followed up.(3) The following case series were presented in order to explain how filiation activities were performed in Kayseri and in our country.
Case Series
1st Case
SuY, SY, AY, ÖY, Eİ and Fİ travelled in the same car from Istanbul to Kayseri in the last week of March, 2020. AY, NY, ÖY and SuY stayed at the house of SuY’s grandmother, HK (62 years old), and grandfather, AK (65 years old). SuY’s paternal grandmother, SY, stayed at her other son’s house (MY). Ninety-one year-old SY was admitted to the hospital with fatigue and loss of appetite on 6th April 2020. COVID RT-PCR test result of the patient who had hypertension and malignancy in her medical history was positive.
On patient’s thorax CT, a pneumonia image compatible with COVID-19 was detected. The patient with moderate general condition and mild respiratory distress was hospitalized. During her follow-ups, the patient’s condition deteriorated, her respiratory distress increased and she was transferred to the intensive care unit. Then, she was exitus on 21 th April 2020.
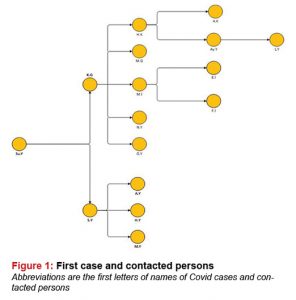
After SY’s positive test result, 5 people with whom she travelled together in the same car were tested for coronavirus. The rapid diagnostic test of fifteen-year old SuY among these 5 people was IgG and IgM positive. On patient’s thorax CT, an image compatible with COVID-19 was reported. The patient had no additional disease in her medical history. Oseltamivir treatment was started and she was followed up. As general condition of the patient was good she was discharged with the recommendation of 14-day household-isolation. During her follow-ups by the family physician, she had no symptoms (Figure 1).
Other people who travelled with SY in the same car were investigated by the filiation team. COVID RT- PCR test result of SY’s son, AY, among these people was positive. As the patient’s thorax CT was normal and his general condition was good he was followed up with household-isolation.
After SY’s positive test result and diagnosis, her other son, MY (67 years old), and his wife, HY (62 years old), were tested with RT-PCR test for COVID-19 as SY stayed in their house. Their test results were negative. Their thorax CT were normal and they were followed up with household-isolation.
COVID RT-PCR test result of 78-year-old KG from family G detected to be in contact with SuY was positive. He had hypertension and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in his medical history. His thorax CT was compatible with pneumonia. Hydroxychloroquine treatment was started. General condition of the patient was normal during his hospital stay and he had no respiratory distress. His repeated COVID RT- PCR test result was negative and he was discharged with recommendation of household-isolation. He had no symptoms during his 14-day home follow-up by the family physician.
People in contact with KG and SuY were investigated and among these people, a 62-year-old woman, HK (grandmother of SuY), was admitted to the hospital with fever, cough and joint pain. Her COVID RT-PCR test result was positive. She was followed up at home as her general condition was good, but her cough increased during follow-up and she was readmitted to the hospital. The patient was diagnosed with COVID-19 pneumonia and hospitalized and hydroxychloroquine treatment was started. As her general condition was good, her saturations were normal and her repeated COVID RT-PCR test result was negative she was discharged from hospital and followed up at home. No problem was experienced during his home follow-ups.
MI (wife of FI), a 41-year-old female patient, had contact history with SuY and KG. KG had contact with his son MG, as well. Test results of MI, KG and MG were positive and persons without any follow-up problems completed their quarantine periods at home. 22-year-old ÖY and 43-year-old NY, who had contact with a case, were determined to be RT-PCR positive. They were followed up at their homes and their quarantine period was completed without any further problems.
PCR test result of FI, the husband of MI, was negative. PCR test result of 19-year-old EI, the daughter of FI and MI living in the same house, was positive. As the patient had no history of an additional disease and her thorax CT was normal she was followed up at home with recommendation of household-isolation.
Since 37-year-old AyY, the other daughter of HK, had a contact history she was tested with PCR for COVID-19 and her test result was positive. PCR test result of 39-year-old male patient, LY, the husband of Ay Y, was positive since he had contact history. As the patients had no history of an additional disease and his general condition were good they were followed up at home with the recommendation of household-isolation.
AK, the husband of HK living in the same house with him, was admitted to the hospital with cough and joint pain. The patient had ischemic heart disease in his medical history but his general condition was good. Therefore, he was followed up at home. However, as his complaints increased he was readmitted to the hospital. His thorax CT was compatible with COVID-19 and he was hospitalized with the diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia. Hydroxychloroquine treatment was started and he was followed up as in good general condition. He was discharged as cured.
2nd Case
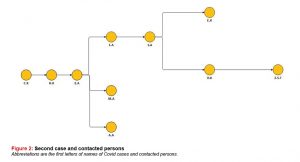
A 49-year-old male patient, HK, travelled from France to Kayseri for his father’s funeral on 10th March 2020. He received visitors expressing their condolences in Akmescit village between 10th-17th March 2020. CK, the uncle of HK, was admitted to the hospital as he had symptoms after he came back from Umrah and his
COVID RT-PCR test result was positive. Since general condition of the patient deteriorated and respiratory distress occurred the patient was exitus on 1st of April. As a result of the methods used for filiation, it was learned that HK had in contact with his sister, EA, and it was found that EA had symptoms. Although COVID RT-PCR test result performed during hospital admission was negative her thorax CT showed findings compatible with COVID-19.
HK was admitted to the pandemic clinic due to his complaints of fever, joint pain and cough. Thorax CT of the patient who had diabetes mellitus in his medical history showed findings compatible with COVID-19. His rapid diagnostic test result was positive. Individuals from this family in contact with EA were investigated and MA, AA and FA who were found to be in contact with EA were tested with rapid diagnostic test and their results were positive. COVID RT-PCR test result of SA, the wife of FA, was also positive (Figure 2).
Since HK and his son, EK, who were related by affinity to the mentioned family had contact history they were tested with RT-PCR for COVID-19 and their results were positive. It was learned that his sister, ZST, looked after him after HK got sick. The result of COVID RT-PCR test performed for ZST as a part of filiation activities was positive. As these two families were related by close affinity to each other and they were crowded families Akmescit village with the population of 1,557 was quarantined on 19th April 2020.
3rd Case
A 62-year-old male patient who works as a driver in the factory, YK, was admitted to Kayseri Private Melikgazi Hospital with headache, shortness of breath, cough and increasing temperature on 11.04.2020. He was hospitalized with the suspect of COVID-19 in- fection and his thorax CT showed findings compatible with COVID-19 infection. Then, as a result of the detailed anamnesis obtained by hospital staff, the patient’s family, co-workers and other possible contacts were included in the Community Health Management System in order to be evaluated by the filiation team of Melikgazi district. On the same day, the filiation team of Melikgazi district made the routine phone calls before fieldworks performed to follow up the possible contacts of the patient. Later in the same day, the team learned that the main case’s wife (NK) and little son (EK) in contact with him were hospitalized in Kayseri City Hospital as they had symptoms and that their thorax CT showed findings compatible with COVID-19 infection.
As a result of detailed investigation by the filiation team of Melikgazi district, the main case’s older son (YK), his older son’s wife (BK) and his grandson (YCK) were quarantined at home and the required filiation procedure was performed. As all members of the family had symptoms on the second day of household quarantine (13th April 2020) they were hospitalized in Kayseri City Hospital and their thorax CT showed findings compatible with COVID-19 infection. After it was found that the mentioned large family was infected all the possible contacts were evaluated by the filiation team of Melikgazi district.
The grandson’s other grandmother (LT) and uncle (AT) in contact with him were quarantined at home. However, since these individuals were living in Incesu district the filiation team of Melikgazi district got in contact with the filiation team of Incesu district through the Community Health Management System and the contacts were followed up by the filiation team of Incesu district.
4th Case
FT was admitted to a healthcare center with cough and fever on 03th April 2020. COVID RT-PCR test result of the patient was positive. She had no disease in her medical history. As she had mild symptoms home follow-up was determined for her. When people in contact with FT were investigated by the filiation team GG and EG were detected to be in contact.
Contact isolation was applied to GG. His rapid diagnostic test result was negative. However, it was found during investigation that he had joint pain and cough 2 weeks ago. In backward investigation, it was found that his mother and father also had symptoms. As EG had contact with her brother, GG, she was tested with rapid diagnostic test and the result was IgM and IgG positive. As the patient had no symptoms she was followed up at home with recommendation of contact isolation. As GG’s mother, ZG, had contact with her son and had symptoms she was tested with RT-PCR for COVID-19 and the result was positive.
After her thorax CT showed findings compatible with COVID-19 and pneumonia was detected she was hospitalized. Hydroxychloroquine was started and the patient’s general condition was good during follow-up. It was found in the filiation follow-up of GG, EG and ZG that father OG was the initial case and infected his wife and children. As the patient’s general condition was good she was followed up at home with recommendation of household isolation. When the source of infection in OG was investigated it was found that he was working in the tea shop of municipal stations and other positive cases were detected in the same workplace. All the people working in this station were quarantined.
Discussion
Following the first case spotted in China, fight against COVID-19 continues throughout the world. Different practices were implemented in different countries for controlling the pandemic.(4) There are studies that report 12-17% of diagnosed patients were hospitalized. This situation has brought a serious burden for healthcare systems.(5,6)
During COVID-19 pandemic, in order to decrease the risk of contagion and to isolate sick individuals from healthy individuals, quarantine and isolation protocols were begun to be implemented by the Ministry of Health.(7) In our study, we observed that risk of contagion could be decreased, in case of rapid and effective implementation of early isolation and quarantine.
In the first case that presented, 11 persons were infected with COVID-19 and 3 persons have become contacted, as a result of one infected person. Moreover, one person became exitus because of COVID-19. Also in second and third cases, many people were infected and one person became exitus, as a result of one person to get ill.
In the study we conducted, it was seen that, in symptomatic cases, PCR tests were detected to be positive within one week of the observance of first symptom. Result of the test is affected by the time of application after the occurrence of symptoms and the day PCR is taken from the onset of the symptoms. In a study conducted in China with 610 cases, sample results from different moments during the disease period were determined to show variability.(8)
In our country, cases were seen especially in middle-aged and older persons. Our cases were also generally from middle-age group. In a seroprevalence study conducted on 50.000 persons in Spain, seroprevalence positivity in 20-49 age group was spotted to be higher than patients of other ages.(9) In a study analysing age distribution of positive cases, middle-age group was shown to contract the disease more commonly.(10)
In a great majority of our cases, it was detected that there was a person diagnosed with COVID-19 among his/her family, relatives or colleagues, or there was a history of travel. Intra-familial contact is important regarding contagion.(11) Following the rules in crowded spaces like workplaces would decrease the risk of contagion. Entrances from and exits to other provinces, as well as violation of social distance rules, were also observed to be effective in spread of the infection.(12) After spotting the cases, contacts were examined with an effective filiation study, new cases were determined with samples taken and further contagion was prevented.
Cases were observed to have symptoms, such as headache, dyspnoea, coughing and increase in body temperature; and PCR tests were taken from these persons. In literature, where first hospital application symptoms and symptoms of hospitalized cases were analyzed, fever, dry cough and dyspnoea were ranked first.(13)
In the case of PCR tests to result negative; suspicious cases were done thorax computerized tomography (Thorax CT), and filiation and isolation implemented on cases compatible with COVID-19. In many studies, importance of thorax CT was mentioned;(14, 15) in the first days of the pandemic, every case that showed typical involvement in scans were hospitalized. We consider that sharing experiences of filiation of COVID-19 cases of different regions can contribute to the controlling of the pandemic. These contributions may offer insights for studies that are being conducted. They may provide a better understanding for the process and may help observing the effectiveness of measures in prevention of the spread of the virus.
Conclusion
Referanslar
- Ergönül Ö. Enfeksiyon Hastalıkları Epidemiyolojisi. Okmeydanı Tıp Dergisi 2016; 32(Ek sayı):1-7. doi:10.5222/otd.2016.001
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. The Lancet 2020; 395(10223): 497-506. doi: 10.1016/ S0140-6736(20)30183-5.
- Bulaşıcı Hastalıklar İle Mücadele Rehberi 2020. https://hsgm. saglik.gov.tr/dosya/mevzuat/genelge/Bulasici-Hastaliklar- ile-Mucadele-Rehberi-Genelgesi-2017-11.pdf, adresinden 01/05/2020 tarihinde erişilmiştir.
- Kamerlin SCL, Kasson PM. Managing Coronavirus Disease 2019 Spread With Voluntary Public Health Measures: Sweden as a Case Study for Pandemic Control. Clin Infect Dis 2020;71(12):3174-81. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa864. PMID: 32609825; PMCID: PMC7337695.
- CDC COVID-19 Response Team. Severe Outcomes Among Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) – United States, February 12-March 16, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2020 (Mar 27);69(12):343-6. doi: 10.15585/mmwr. mm6912e2. PMID: 32214079; PMCID: PMC7725513.
- Taglicher lagebericht des RKI zur coronavirus-krankheit-2019 (COVID-19). Berlin: Robert Koch Institute, 2020. https:// www.rki.de/DE/ Content/InfAZ/N/Neuartiges_Coronavirus/ Situationsberichte/2020-05-12-de. pdf?__blob=publicationFile, adresinden 12/10/2020 tarihinde erişilmiştir.
- Covıd-19 (Sars-Cov-2 Enfeksiyonu) Genel Bilgiler, Epidemiyoloji Ve Tanı. https://covid19bilgi.saglik.gov.tr/depo/rehberler/covid-19-rehberi/Covıd-19_Rehberı_Genel_Bılgıler_ Epıdemıyolojı_Ve_Tanı.pdf, adresinden 17/06/2020 tarihinde erişilmiştir.
- Li Y, Yao L, Li J, Chen L, Song Y, Cai Z, Yang C. Stability issues of RT-PCR testing of SARS-CoV-2 for hospitalized patients clinically diagnosed with COVID-19. J Med Virol 2020 ;92(7):903- 8. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25786. Epub 2020 Apr 5. PMID: 32219885; PMCID: PMC7228231.
- Pollán M, Pérez-Gómez B, Pastor-Barriuso R, Oteo J, Hernán MA, Pérez-Olmeda M, et al. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in Spain (ENE-COVID): a nationwide, population-based seroepidemio- logical study. Lancet. 2020 (Aug 22);396(10250):535-44. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31483-5.
- Bulut C, Kato Y. Epidemiology of COVID19. Turk J Med Sci 2020;50:563-70.
- Durusoy R, Ata A, Geçı̇m C, Fı̇lı̇s N, Fı̇dan E, Şı̇mşek S, et al. Ege Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi Hastanesi’nde COVID-19 vakalarının sürveyansı, filyasyonu ve temaslılarının belirlenmesi. Turkish Journal of Public Health 2020; 18(COVID-19 Special): 25-39. doi: 10.20518/tjph.771286.
- Nicola M, Alsafi Z, Sohrabi C, Kerwan A, Al-Jabir A, Iosifidis C, et al. The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19): A review. Int J Surg 2020;78:185-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.04.018.
- Wiersinga WJ, Rhodes A, Cheng AC, Peacock SJ, Prescott HC. Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review. JAMA 2020 (Aug 25);324(8):782-93. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12839.
- Caruso D, Zerunian M, Polici M, Pucciarelli F, Polidori T, Rucci C, et al. Chest CT Features of COVID-19 in Rome, Italy. Radiology 2020;296(2):79-85. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020201237.
- Chung M, Bernheim A, Mei X, Zhang N, Huang M, Zeng X, et al. CT Imaging Features of 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019- nCoV). Radiology 2020;295(1):202-7.